Sinus floor elevation, Xenograft, Autogenous bone, Collagen membrane, Osteoconductivity
Fig. 7. Box-plot representing the new bone percentage and standard deviations (whiskers) found in the various regions evaluated after 8 weeks of healing. (*), a statistical significant difference : Influence of the use of autogenous bone particles
author: Giacomo Favero, Jose Via-Almunia, Carmen Carda, Jos Javier Martn de Llano, Berta Garca-Mira, David Soto-Pealoza, Miguel Pearroch | publisher: drg. Andreas Tjandra, Sp. Perio, FISID
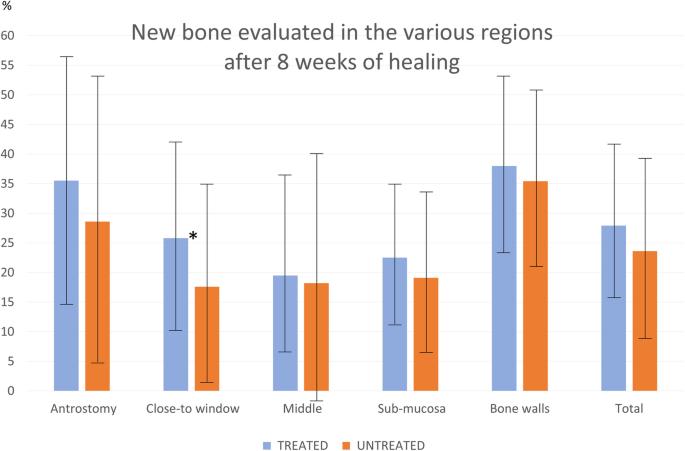
Fig. 7. Box-plot representing the new bone percentage and standard deviations (whiskers) found in the various regions evaluated after 8 weeks of healing. (*), a statistical significant difference
Serial posts:
- Fig. 6. Photomicrographs of decalcified sections illustrating the healing after 8 weeks. a Treated site. Most of the antrostomies presented remaining defects in the outer contour. b, c Untreated sites. Two antrostomies of the treated sites and four of the untreated sites appeared not closed with corticalized bone and presented connective tissue interposed between the edges of the antrostomy. Scarlet-acid fuchsine and toluidine blue stain. a Image grabbed at × 20 magnification. b, c Images grabbed at × 40 magnification : Influence of the use of autogenous bone particles
- Fig. 7. Box-plot representing the new bone percentage and standard deviations (whiskers) found in the various regions evaluated after 8 weeks of healing. (*), a statistical significant difference : Influence of the use of autogenous bone particles
- Fig. 8. Photomicrographs of decalcified sections. a Untreated site. Woven bone formed from the sinus walls after 1 week of healing. b Treated site. After 8 weeks, woven bone was still found forming ridges towards residues of provisional matrix, showing that the healing was not completed yet. Scarlet-acid fuchsine and toluidine blue stain. a × 100 magnification. b × 20 magnification : Influence of the use of autogenous bone particles