The trabecular bone is located between the alveolar bone proper and the cortical bone plates.
Trabecular bone
author: Nikos Mardas | publisher: drg. Andreas Tjandra, Sp. Perio, FISID
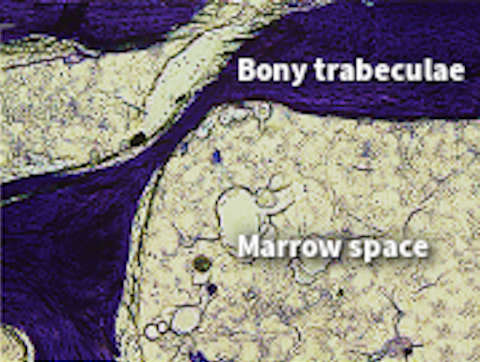
The trabecular bone is located between the alveolar bone proper and the cortical bone plates. Trabecular bone, also known as cancellous bone, consists of bony trabeculae and marrow spaces. In adult patients the marrow spaces are rich in adipocytes and mesenchymal cells. Mesenchymal cells have bone-forming potential and may be induced to form bone, but they also support the differentiation of hemopoietic cells into osteoclasts that will initiate bone resorption.
Serial posts:
- Healing extraction socket
- Resorption modifies alveolar ridges
- Anatomical features of the alveolar process
- Forming alveolar ridge
- Alveolar process: function and development
- Parts of alveolar process
- Different terms for the alveolar bone proper
- Lamina dura
- Alveolar bone proper: Attachment apparatus
- Bundle bone
- Alveolar bone proper
- Supporting bone
- Outer cortical plate
- Cortical bone
- Trabecular bone
- Macroanatomy of alveolar process
- Extraction socket
- Extraction socket wall
- Alveolar ridge
- Ridge of edentulous site