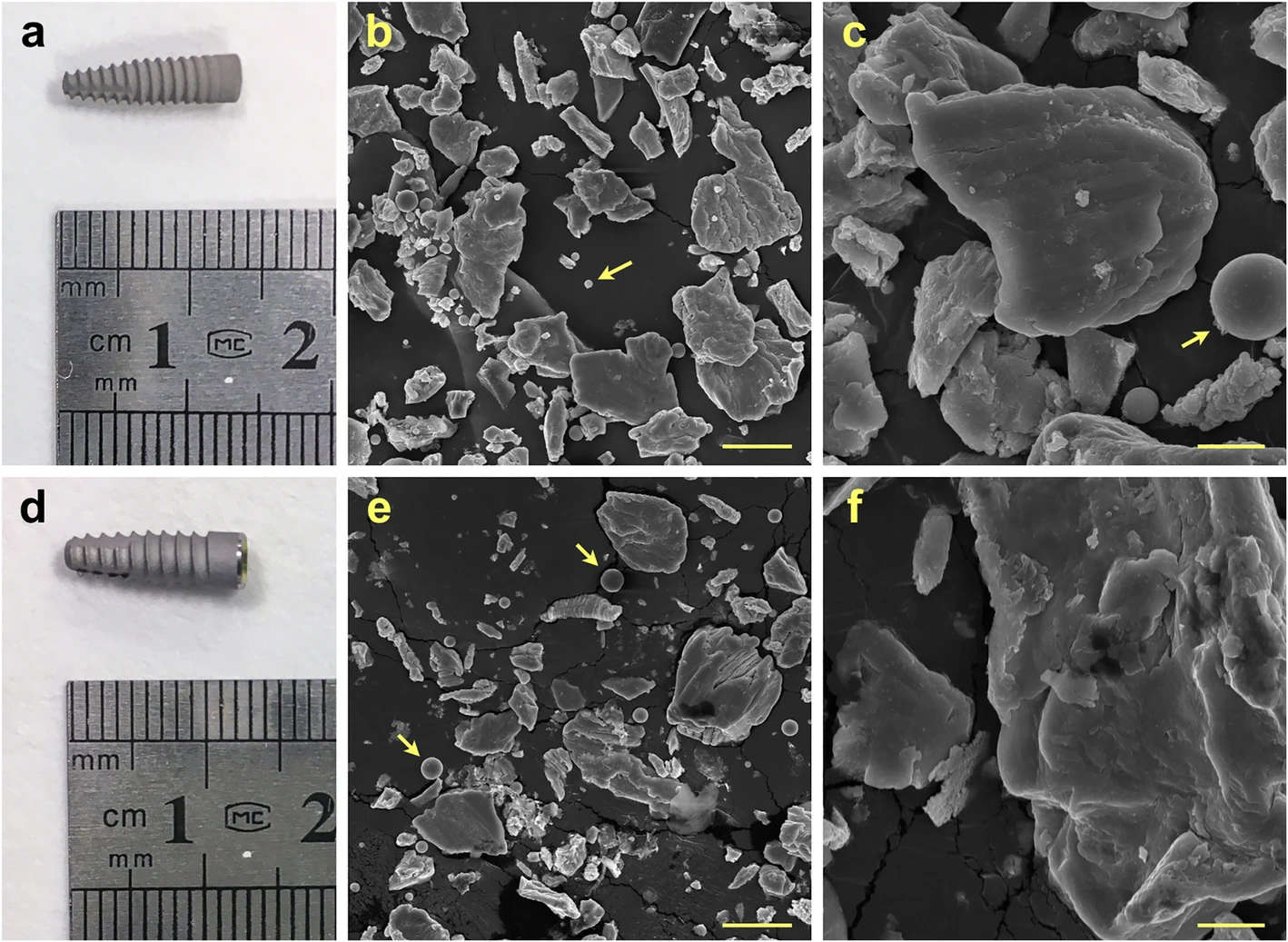
Figure 1. Representative photo of implants and SEM images of particles produced by mock implantoplasty procedure. a–c Straumann 021.4512, bone level, diameter 4.1 mm, regular CrossFit®, SLA® 12 mm Roxolid® (commercially pure grade 4 titanium). d–f Biohorizons PBR 50105, RBT 5.0 × 10.5 mm, 5.7 Platform (grade 5 titanium alloy). Arrows indicate titanium oxide spheres. Scale bar represents 20 and 5 μm for low and high magnification respectively
Figure 1. Representative photo of implants and SEM images of particles
author: Fadi N Barrak, Siwei Li, Albert M Muntane Julian R Jones | publisher: drg. Andreas Tjandra, Sp. Perio, FISID
Serial posts:
- Particle release from implantoplasty of dental implants and impact on cells
- Background : Particle release from implantoplasty of dental implants (1)
- Background : Particle release from implantoplasty of dental implants (2)
- Materials & methods : Particle release from implantoplasty of dental implants (1)
- Materials & methods : Particle release from implantoplasty of dental implants (2)
- Materials & methods : Particle release from implantoplasty of dental implants (3)
- Results : Particle release from implantoplasty of dental implants
- Discussion : Particle release from implantoplasty of dental implants (1)
- Discussion : Particle release from implantoplasty of dental implants (2)
- Discussion : Particle release from implantoplasty of dental implants (3)
- Discussion : Particle release from implantoplasty of dental implants (4)
- Figure 1. Representative photo of implants and SEM images of particles
- Figure 2. EDX spectra of particles produced by the mock implantoplasty procedure
- Figure 3. Titanium (Ti) and vanadium (V) release from the particles
- Figure 4. Titanium (Ti) and vanadium (V) content in DMEM
- Figure 5. The effect of grade 4 and grade 5 implant particles