Figure 2. a SEM image, ×10,000, demonstrating the characteristic porous surface of selective infiltration etching surface of zirconia. b SEM image, ×500, demonstrating deposition of PRP coat and complete filling of the porous surface. c SEM image, ×500, demonstrating filling of the porous surface with particles of HA
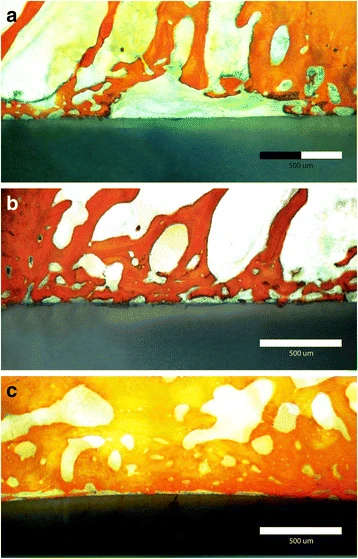
Figure 3. Stained histomorphometric section
author: Dawlat Mostafa, Moustafa Aboushelib | publisher: drg. Andreas Tjandra, Sp. Perio, FISID
Figure 3. a Stained histomorphometric section demonstrating bone implant contact of uncoated zirconia implant. b Stained histomorphometric section demonstrating bone implant contact of HA–hybrid–zirconia surface. c Stained histomorphometric section demonstrating bone implant contact of PRP–hybrid–zirconia surface
Serial posts:
- Bioactive–hybrid–zirconia implant surface
- Background : Bioactive–hybrid–zirconia implant surface
- Methods : Bioactive–hybrid–zirconia implant surface
- Results : Bioactive–hybrid–zirconia implant surface
- Discussion : Bioactive–hybrid–zirconia implant surface
- References : Bioactive–hybrid–zirconia implant surface
- Figure 1. Mercury porosimetry and the average pore diameter of the prepared implants
- Figure 2. SEM image, ×10,000, demonstrating the characteristic porous surface
- Figure 3. Stained histomorphometric section
- Figure 4. Bone implant contact of different test groups