Figure 3. Evaluation of programmed cell death (apoptosis) in dental stem cells. (A) Flow cytometry analyses (for details materials and methods) show percentage of vital cells (black number), apoptotic cells (blue number), and dead cells (red number). (B) Western blot analyses show the expression of the pro-apoptotic marker BAX and the anti-apoptotic marker BCL2.
Figure 4. Osteogenic differentiation of dental stem cells
author: Martin Gosau,Sandra Viale-Bouroncle,Hannah Eickhoff,Esthera Prateeptongkum,Anja Reck,W Gtz,Christoph Klingelhffer,Steffen Mller, | publisher: drg. Andreas Tjandra, Sp. Perio, FISID
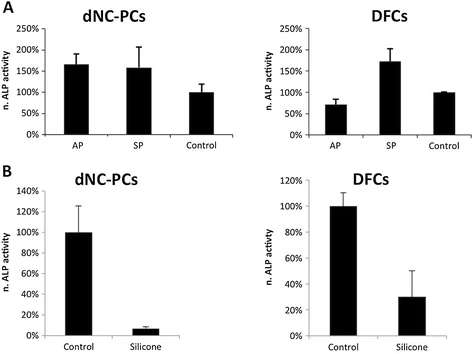
Figure 4. Osteogenic differentiation of dental stem cells. Normalized ALP activity of dNC-PCs and DFCs on AP and SB (A) and on silicone (B). Cells were differentiated on standard cell culture dishes for control.
Serial posts:
- Evaluation of implant-materials as cell carriers for dental stem cells under in vitro conditions
- Background : Evaluation of implant-materials as cell carriers for dental stem cells
- Methods : Evaluation of implant-materials as cell carriers for dental stem cells (1)
- Methods : Evaluation of implant-materials as cell carriers for dental stem cells (2)
- Methods : Evaluation of implant-materials as cell carriers for dental stem cells (3)
- Methods : Evaluation of implant-materials as cell carriers for dental stem cells (4)
- Results : Evaluation of implant-materials as cell carriers for dental stem cells
- Discussion : Evaluation of implant-materials as cell carriers for dental stem cells (1)
- Discussion : Evaluation of implant-materials as cell carriers for dental stem cells (2)
- Figure 1. Cell attachment on tested materials.
- Figure 2. Cell proliferation of dNC-PCs and DFCs on tested materials
- Figure 3. Evaluation of programmed cell death (apoptosis) in dental stem cells
- Figure 4. Osteogenic differentiation of dental stem cells
- Figure 5. Evaluation of osteogenic differentiation
- Figure 6. Cultivation and osteogenic differentiation of DFCs on PA