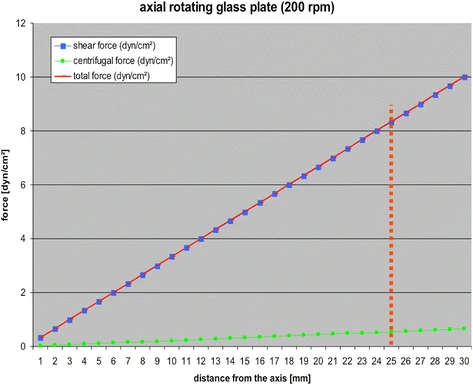
Figure 3. Diagram for visualisation of the calculation of shear stress rates taking into account the centrifugal force and the glass plates’ dimensions. For example, at a distance of 25 mm from the centre of the upper plate, the shear forces’ value is 8.33 dyn/cm2, together with an additional centrifugal force that has a value of 0.55 dyn/cm2
Figure 3. Diagram for visualisation of the calculation of shear stress rates
author: P W Kmmerer,D G E Thiem,A Alshihri,G H Wittstock,R Bader,B Al-Nawas, M O Klein | publisher: drg. Andreas Tjandra, Sp. Perio, FISID
Serial posts:
- Cellular fluid shear stress on implant surfaces
- Methods : Cellular fluid shear stress on implant surfaces (1)
- Methods : Cellular fluid shear stress on implant surfaces (2)
- Methods : Cellular fluid shear stress on implant surfaces (3)
- Results : Cellular fluid shear stress on implant surfaces (1)
- Results : Cellular fluid shear stress on implant surfaces (2)
- Discussion : Cellular fluid shear stress on implant surfaces (1)
- Discussion : Cellular fluid shear stress on implant surfaces (2)
- Discussion : Cellular fluid shear stress on implant surfaces (3)
- Discussion : Cellular fluid shear stress on implant surfaces (4)
- References : Cellular fluid shear stress on implant surfaces
- Figure 1. Three-dimensional illustration and photography
- Figure 2. Side view of a computerized simulation
- Figure 3. Diagram for visualisation of the calculation of shear stress rates
- Figure 4. Randomly orientated osteoblasts without influence of rotation
- Figure 5. Osteoblasts with an orientation tendency after 24 h